Key Takeaways: What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?
- Cloud storage has many uses, including data storage, file sharing and collaborating with others.
- Four cloud storage models exist: public, private, hybrid and multicloud.
- Cloud storage pricing varies depending on the provider, including everything from free plans and trials to expensive, full-feature plans.
Cloud storage is a service that helps to free up space on your device by letting you store your files in the cloud. You can access your files from anywhere as long as you have an internet connection. There are plenty of cloud storage options available, as we discuss in our best cloud storage services article. However, let’s answer one question first: What is cloud storage and how does it work?
Using cloud storage offers many benefits. One example is that you can easily access and share your files with almost anyone. Another is security: While stored on remote servers, security protocols and user account settings keep your data protected. However, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. We’ll discuss cost, use cases and the different types of cloud storage available.
What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?
Cloud storage is a service that allows you to store data online in a network of remote servers, also known as the cloud. Without cloud storage, you must keep your data on your computer, an external hard drive or a flash drive. This means you have limited space available. You can run into issues or lose your data if your external hard drive fails.
You can transfer data stored on your computer to your cloud storage account, freeing up disk space.
Since your data is stored on a remote server, you only need an internet connection to access it. Most cloud storage services have downloadable apps for desktop or mobile, giving you plenty of flexibility to access your files.
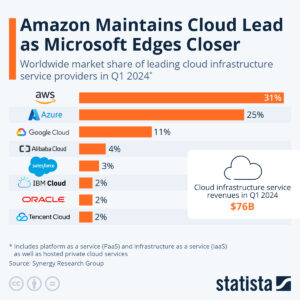
How Does Cloud Storage Work? Models Explained
There are four models for cloud storage: public, private, hybrid and multicloud. Public servers are generally cheaper and more scalable, while private servers are usually more secure and reliable.
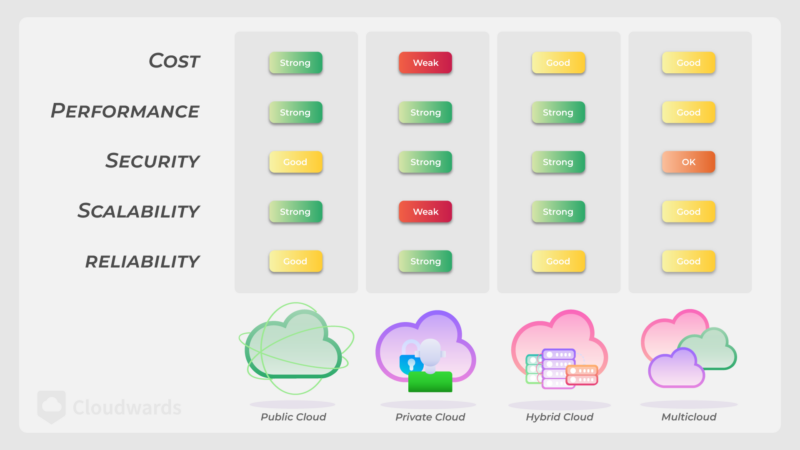
Cloud storage systems come in four models: public, private, hybrid and multicloud.
Spreading your data across multiple services can reduce downtime or data loss while improving flexibility. Because of this, some organizations will choose a hybrid or multicloud model. Here are the four models in more detail.
| Features: | Public | Private | Hybrid | Multicloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Very good, using a pay-as-you-go model | Good, though upfront infrastructure and continuing maintenance costs could add up | Average, as you pay for a service and maintain your own data storage infrastructure | Could be costly with more than one provider, depending on organizational requirements |
| Performance | Typically good but dependent on provider uptime | Usually very good, as downtime is limited since there’s no need to connect to remote servers | Generally good, particularly with localized cached data | Can vary due to the need to depend on multiple remote servers that require internet connectivity |
| Security | Good but dependent on the provider’s security measures | Good for security, as hardware and software are localized | Typically has good security, with a mix of internal and provider security measures | Security conflicts may exist with multiple cloud providers |
| Scalability | Very scalable | Some scalability issues are possible. | Very scalable | Moderately scalable; could be cost-prohibitive |
| Reliability | Internet connection dependent | Very reliable, as the infrastructure is on-premise | Local data is readily available; off-site cloud storage is dependent on internet connectivity. | Primarily internet connection dependent, mitigated with a mix of private cloud capabilities |
Public
Public cloud storage is perhaps the most common or at least the most familiar type of cloud storage. For example, if you have an account with Box.com — which we cover in more detail with our Box Business review — then you are using public cloud storage.
Public cloud storage users share server space with each other. Public cloud storage can adjust server capacity if demand increases or decreases.
Private
Private cloud storage works very similarly to public cloud storage, with the main difference being that server space is not shared with outside organizations or individual users. Anyone who uses private cloud storage has their own servers and data centers to store and manage data. Organizations can negotiate with public cloud providers to procure dedicated server space.
Hybrid
A hybrid cloud storage solution is like a combination of public and private cloud models. Larger businesses and organizations are most likely to use a hybrid configuration. With a hybrid cloud storage model, organizations have more flexibility in deciding where to store their data. Sensitive data could go on private servers, while team project files could go on public servers.
Multicloud
A multicloud model combines more than one cloud storage service using public, private or a combination of both models. There are a few reasons why an organization, or even an individual, would choose a multicloud model.
A good example is an organization choosing a cloud storage provider because of other features it might offer while also using a provider in a different country if the organization has a global workforce.
Pros of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage offers many benefits and advantages over storing data locally. Examples include cost, security and flexibility, as you will see below.
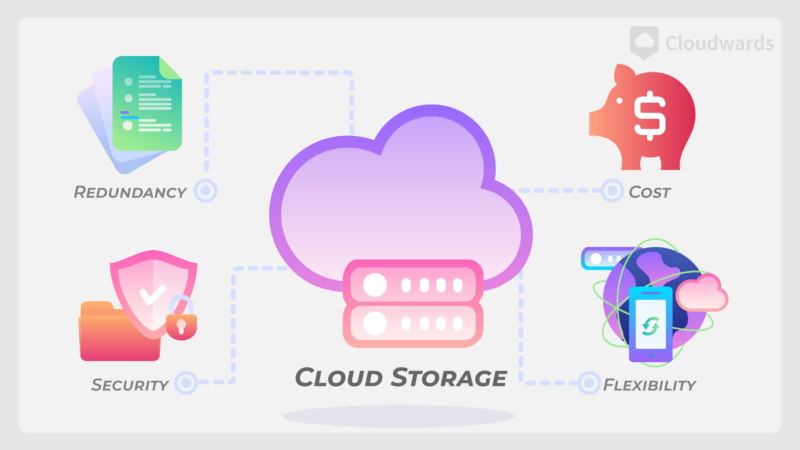
The main benefits of cloud storage can be broken into four categories.
Cost
Choosing a cloud storage provider means that businesses or individuals don’t have to worry about infrastructure costs and maintenance. Most will only pay for the amount of storage needed and can reallocate costs and resources to other areas.
Security
It is rare to find a cloud storage provider that doesn’t have robust security protocols and protected data centers. Most cloud storage services also have user-controlled security settings, such as two-factor authentication.
Some cloud storage takes security and privacy a step further by offering zero-knowledge encryption. Zero-knowledge encryption ensures that only you can access your account, as only you have the password to decrypt it.
Flexibility
Most cloud storage services offer tools and features that let you access and work with your data in various ways. Options include multiple file-sharing methods, different ways to keep your account in sync and flexibility with version control.
Redundancy
Redundancy is essential to cloud storage, as it provides a fail-safe against data loss. With redundancy, data is replicated on multiple servers, often at different locations. Should a disaster happen at one location, cloud storage solutions are able to recover.
Challenges of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is not a perfect solution, especially when using a public model. Privacy and compliance are two of the more significant challenges that individuals and organizations face.
Privacy
Though all cloud storage services collect data when you sign up or use the service, the provider you choose significantly impacts your privacy. Sync.com is an excellent example of a cloud service that collects the minimum amount of data necessary. Check out our Sync.com review for more information.
Conversely, Google is notorious for collecting data on you and how you use its services. We cover more in our Google Drive review. Simply put, anyone who uses Google’s products becomes part of its analytics machine.
Compliance
Not all industries can use any cloud provider they want due to regulatory compliance issues. A good example is companies in the healthcare or financial sector. Any company with strict data compliance rules should be aware that some cloud storage solutions may not comply with their company or industry regulations.
Latency and Speed
Using a cloud storage solution puts you at the mercy of how fast it can process data. Cloud services with slower upload or download speeds could impact your productivity. Speed is a factor — if that’s a priority for you, check out our article on the fastest cloud storage providers.
Similar to speed, latency could also be a factor. Latency happens when network traffic — either yours or the cloud storage provider’s — becomes congested and slow.
Availability
Despite cloud storage solutions’ best efforts, it is impossible for any of them to have 100% uptime all the time. If a service goes down, you are at the cloud provider’s mercy to restore services. You can’t access your data while it is down. Downtimes are rare, but they can happen.
Cloud Storage Use Cases
Cloud storage use cases go beyond simply sharing files and storing data, regardless of whether you have personal or professional needs. It plays a crucial role in various business applications, including point-of-sale systems.
Disaster Recovery and Backup
Using cloud storage for backup or disaster recovery is a great use case example. Data loss can happen due to several factors, including human error or cyberattacks. Using a cloud storage solution to store some or all of your data instead of keeping it locally helps prevent data loss in the event of an unforeseen event or failure.
Online backup services are another category of cloud products. Similar to cloud storage, online backup provides a dedicated way to back up large amounts of data. Read our article on the best online backup services for more details.
Archive
Cloud storage is a great way to offload older or archival data taking up space on local hard drives or servers. Companies in certain industries, like financial services or law firms, often need to keep data for many years for research or audit purposes. Storing data with a cloud storage solution is a great way to maintain access while freeing up space for relevant data.
Project Management
Cloud storage is a useful tool for large, complex or virtual teams to manage project files. Depending on the cloud storage solution, teams could have access to additional productivity and collaboration tools. A few examples include tagging folders or files, adding comments and creating tasks.
Another benefit of cloud storage while working on project documents is sharing files. Files can be shared internally to a team or externally if needed. Most cloud storage providers let you invite others directly with an email address or create a shareable link.
Analytics
For some, using cloud storage to hold data for analytical purposes is easier and more cost-effective. As data grows, cloud storage provides a scalable option that’s accessible and secure.
Data lakes are large-scale cloud storage solutions designed for analytics. When data lakes use the object storage type — defined in the next section — it doesn’t alter the data. Object storage also includes metadata, which is often used when running analytical reports.
The Three Types of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage comes in three types: object storage, file storage and block storage. What you need from a cloud storage solution will determine the type of service you choose.
File Storage
File storage is commonly used on computers and external hard drives. It organizes and stores data using a hierarchical method at the file level. Network-attached storage (NAS) devices also use the file storage type. Read our best NAS cloud backup article if you need this capability.
Simply put, data is stored in files and often organized into folders. You can find these folders and files with directories and sub-directories. Open Finder on a Mac or File Explorer on Windows and you’ll see the file storage type in action.
Block Storage
Block storage gets its name from how it disassembles and stores a file. With block storage, files are broken down into equal-sized blocks, and each block is stored individually with a unique identifier or address. Compared to file storage, block storage is faster and more efficient.
The main difference between block storage and file storage is that block storage does not use the directory/sub-directory/folder method of organization. When you want to access a file, the operating system reassembles the blocks of that file.
Object Storage
Object storage is best used to store vast amounts of unstructured data and is the preferred storage type for building applications. Unstructured data includes files like photos, videos, audio files and web content. These data types are stored in buckets instead of files or blocks, making it easier to customize the metadata.
With object storage, scalability, flexibility and cost are benefits for those who store a large amount of unstructured data.
What Are Cloud Storage Costs Like?
A basic or entry-level plan can cost between $5 and $9 per month, whereas the more advanced plans run anywhere from $20 to $30 per month. Business plans usually cost $15 to $35 per user per month.
Almost all cloud storage services offer a lower monthly price when you pay annually. Some even offer lifetime plans, which we cover in our best lifetime plans article.
For some, a free plan, which many providers offer, is enough to test a service. If you are looking for a free plan, check out our best free cloud storage article. However, a paid plan is the way to go for those needing more storage space.
Cost is one of the most significant factors to consider when getting what you need out of a cloud storage provider. Generally, the higher the price, the more storage and features you get. In most cases, you are purchasing more than just storage space. However, If storage is your only concern, peruse our list of the best unlimited cloud storage providers.
For a deeper dive into costs and plans, read our article on understanding cloud storage pricing.
Final Thoughts
Cloud storage is a flexible and affordable tool to help us manage our growing digital lives. Most of us use the familiar file storage type, though other types are also available. Use cases include data storage for analytics or as a way to protect our data during a disaster.
However, for situations where internet access might be limited, there are also offline cloud storage solutions that offer a similar level of flexibility with the added benefit of local file availability. If cloud storage is a newer concept, hopefully this article demystified what it is and how it works.
FAQ: How Does Cloud Storage Work?
-
Cloud storage allows you to store your data on a remote server, saving space on your local device. Changes you make to your files in the cloud sync with your device and vice versa. Additionally, you can share files with others by directly inviting them via email or by creating a shareable link.
-
Yes. Most cloud storage solutions have several security measures to protect your data. Examples include using AES 256-bit encryption to protect your data from unauthorized access while it is stored on a remote server. TLS/SSL encryption protocols protect your data during transfers from anyone trying to impersonate the recipient.
-
Privacy is one of the larger potential disadvantages of cloud storage. The service provider you choose is a major determining factor. Some cloud storage providers, like Sync.com, are great with privacy. Others, like Google, are not.
-
Yes. Many cloud storage providers offer free plans. pCloud is one example, as it offers up to 10GB of free storage. Read more about it in our pCloud review. MEGA offers the most free storage at 20GB. We cover this and more in our MEGA review.